The Nitty Gritty
- Understand the meaning behind SEER and its importance in the HVAC industry
- Learn how to calculate SEER and EER ratings
- Discover the advantages of having a high SEER rating

Commercial buildings rely heavily on heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to maintain a comfortable and productive environment for employees and customers. However, these systems can also consume significant amounts of energy, contributing to high utility bills and harmful emissions.
While various factors contribute to energy efficiency in HVAC systems, one of the most important aspects to consider is the SEER rating. Does this term sound familiar? If not, this article will provide a complete understanding of HVAC SEER ratings and how they can benefit your business.
What is SEER?
SEER is an acronym that stands for Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio. It is a standard measurement used to determine the energy efficiency of a heating and cooling system.
According to Energy Star, the government-backed program for energy efficiency, "SEER is a measure of equipment energy efficiency over the cooling season."
It compares the amount of cooling a system produces (measured in British thermal units or BTUs) to the amount of electricity it consumes (measured in watt-hours). The higher the SEER rating, the more efficient the system is.
What do HVAC SEER Ratings Mean?
In the HVAC industry, SEER ratings are a significant metric used to indicate a system's energy efficiency. When producing HVAC systems, manufacturers are required by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) to label their products with a yellow EnergyGuide label that displays their SEER rating.
The metrics help consumers make informed decisions when purchasing equipment and help contractors identify the right system for their customers.
Highlights of HVAC SEER ratings
- SEER ratings range from 8 on the low end to 30 on the high end.
- The minimum seer rating 2023 changed from the previous 13 range to 14 as part of DOE's effort to improve energy efficiency standards.
- Increasing the SEER rating by one point can save up to 10-20% on electricity bills.
- SEER ratings only measure an HVAC system's cooling efficiency; other metrics, such as HSPF, measure heating efficiency.
- SEER ratings can be found in four ways: The yellow and black EnergyGuide label on the equipment, a piece of paper attached to the indoor unit, the model number or by contacting the manufacturer.
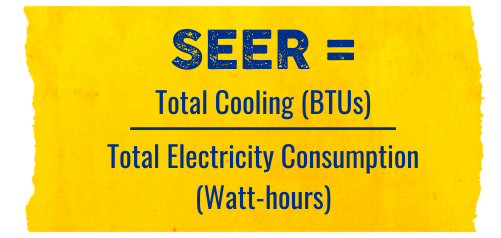
How to calculate SEER
Calculating the SEER rating for an HVAC system is relatively straightforward. Take the total amount of cooling in BTUs divided by the total electricity consumption (in watt-hours) during peak energy usage. The resulting number will be your system's SEER rating.
SEER Calculation Formula
Total Cooling (BTUs) / Total Electricity Consumption (watt-hours)
For Example: If your HVAC system produces 48,000 BTUs of cooling and consumes 5,500 watt-hours (or 5.5-kilowatt hours) during peak usage, your SEER rating would be:
SEER = 48,000/5,500 = 8.73
In this case, the system's SEER rating would be rounded to the nearest whole number, making the SEER rating 9. This means that the system produces 9 BTUs of cooling for every watt-hour of electricity consumed.
SEER vs. SEER2
As an HVAC servicing company, it is crucial to understand the difference between SEER and SEER2 ratings. While they may sound similar, there are significant differences between the two metrics.
As of 1 January 2023, SEER2 has replaced SEER as the standard metric for HVAC energy efficiency. The main difference between the two is that SEER2 considers real-world conditions when testing the efficiency of an HVAC system.
Under SEER, systems were tested in a laboratory setting with controlled conditions, which did not accurately reflect real-life usage. However, under SEER2, tests are conducted in a more rigorous environment that better reflects real-world conditions. This change has resulted in a slight decrease in SEER ratings, making them 4.7% lower than the original SEER ratings.
For example, an HVAC system with an HVAC SEER rating of 16 before 2023 would be equivalent to a SEER2 rating of (16-(0.047*16)= 15.25). This change is essential to note when comparing the efficiency of older systems to newer ones.
Therefore, it is essential to note that all manufacturers must now list SEER2 ratings on their HVAC systems. If you compare a system with a SEER rating before 2023, you must adjust the SEER down by about half a point to get an accurate comparison.
PRO tip: You may want to have SEER2 as a part of your conversation during regular scheduled maintenance visits with your customers. You may want to add this to your visit checklist to ensure your crew is discussing this with customers and ensuring field service technicians are making any adjustments in asset management tools. By keeping customers apprised of these changes, you are showing them your expertise and continue to build credibility.
SEER vs. EER
Another standard metric used in the HVAC industry is the Energy Efficiency Ratio or EER. While SEER and EER both measure the efficiency of an HVAC system, there are some significant differences between them.
Both SEER and EER rates measure energy efficiency, but some main differences exist. SEER measures efficiency over an entire season, while EER only measures efficiency at a single temperature (specifically 95 degrees Fahrenheit).
Additionally, SEER ratings evaluate the efficiency of whole-house HVAC systems, while EER ratings are used to evaluate room air conditioners, such as portable or window units.
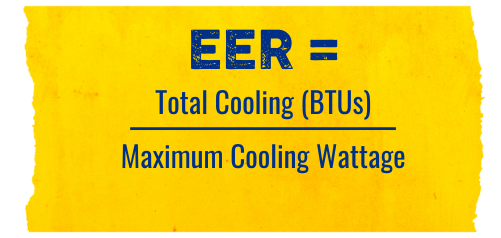
How do you calculate EER?
The equation for calculating the EER is relatively simple. Simply divide the cooling capacity in BTUs by the maximum wattage consumed during peak usage.
EER Calculation Formula
Cooling Capacity (Maximum BTUs)/ Maximum Cooling Wattage
For example, a system with a cooling capacity of 65,000 BTUs and a maximum wattage consumption of 4,800 watts would have an EER of 13.54:
EER = 65,000 / 4,800 = 13.54
As with SEER ratings, the higher the EER rating, the more efficient the system is.
What are the Advantages of a High SEER Rating?
Energy efficiency is essential for several reasons, and having a high SEER rating can offer numerous benefits for the environment and businesses. Below are some advantages of having a high HVAC SEER rating.
Lower electric bills with high SEER
As mentioned earlier, higher SEER ratings result in lower electricity bills. Increasing the SEER rating by just one point can save up to 10-20% on cooling costs.
This is particularly important for commercial businesses operating multiple HVAC systems, as the savings can increase significantly. Additionally, with rising energy costs and an increasing focus on sustainability, having a high SEER rating can help businesses reduce their overall operational costs and stay competitive in the market.
Tax credits and rebates for energy-efficient systems
While high SEER ratings can lead to cost savings on electricity bills, they can also result in additional financial benefits for businesses. Many utility companies offer rebates when upgrading to an HVAC system with a high SEER rating as part of their energy conservation initiatives.
Moreover, the government also offers tax credits for homeowners and commercial businesses that install energy-efficient HVAC systems. According to the Inflation Reduction Act passed in 2022, investing in energy-efficient heating and cooling equipment can result in a 30% tax credit of up to $600. This is a significant incentive for businesses to invest in energy-efficient HVAC systems with high HVAC SEER ratings.
Enhanced cooling efficiency for comfort
HVAC systems with high SEER ratings provide enhanced cooling efficiency for optimal comfort. As technology advances, newer systems are being designed with features like two-stage and variable-speed cooling, which allows for more consistent temperatures throughout multiple floors in a building.
This added comfort can be especially beneficial in creating a comfortable working environment for your employees or customers. Having an HVAC system with advanced technology and a high SEER rating can also improve air quality and reduce humidity levels, further enhancing overall comfort and well-being.
Reducing your carbon footprint
Energy efficiency is not only beneficial for businesses but also for the environment. As an HVAC company, promoting high SEER ratings can help reduce carbon emissions and create a more sustainable future.
With climate change becoming increasingly prevalent, there is a growing demand for energy-efficient solutions. By promoting high SEER ratings and energy-efficient HVAC systems, businesses can play their part in reducing the impact of their operations on the environment.
Budgeting for HVAC Units with High SEER Ratings
Whether you plan to upgrade your existing HVAC system or install a new one, the cost is an essential factor. The good news is that high SEER ratings can lead to long-term cost savings, making them a worthwhile investment for businesses.
However, the cost of HVAC units with high SEER ratings may vary depending on several factors, such as:
- Features and upgrades: As technology advances, older convectional air ducted systems are being replaced with more efficient options like ductless and geothermal systems. While these may have high SEER ratings, they also come at a higher cost.
- The SEER rating itself: High SEER ratings often result in higher upfront costs but can also lead to significant savings in the long run.
- Installation costs: The installation cost can vary depending on your location and the project's complexity. Getting quotes from reputable HVAC companies to determine the cost for your specific needs is essential.
- Tax credits and rebates: Investing in energy-efficient HVAC systems can result in tax credits and rebates, reducing the overall cost for businesses. Research any available incentives in your area when budgeting for a high SEER-rated HVAC unit.
How to overcome customer objections to SEER-Rated Equipment
While high SEER-rated HVAC units can lead to cost savings in the long run, there are also cost-saving strategies that businesses can implement to help customers over the lifetime of the equipment. These include:
- Investing in HVAC software: Dealing with various customers and managing multiple HVAC systems can be daunting. As an HVAC company, investing in HVAC software can help streamline your operations, manage recurring appointments, and improve real-time communication with customers. This can ultimately lead to cost savings and increased efficiency.
- Regular maintenance: Promoting scheduled maintenance to your customers can help keep their HVAC systems running efficiently, preventing costly breakdowns and repairs. Encourage customers to schedule regular maintenance checks and offer discounts for continuous service. In addition, there are many software options that provide asset maintenance features to automate appointments, streamlining your workflow.
- Energy-saving tips: Educate your customers on how to use their HVAC systems more efficiently, such as using programmable thermostats and adjusting temperatures when not in use. This can help reduce energy consumption and lead to cost savings.
- Educate customers on SEER ratings: What is SEER rating? Many customers may not understand the importance of SEER ratings in HVAC systems. As an HVAC company, educate your customers on the benefits of high SEER ratings and how it can help them save money in the long run.
Final thoughts about HVAC SEER ratings
SEER ratings play a crucial role in determining the energy efficiency of HVAC systems. Promoting high SEER-rated systems to your customers leads to long term cost savings and contributes to a more sustainable future.
Additionally, investing in HVAC software and implementing cost-saving strategies can help you manage your operations more efficiently and minimize operational costs. With the growing demand for energy-efficient solutions, it’s important to stay updated on SEER ratings and educate your customers on its benefits.
Contact us today and try out our HVAC software to streamline your operations and stay ahead.